Propiedades de la integral definida
De Wikillerato
| Línea 13: | Línea 13: | ||
\, = \, | \, = \, | ||
\int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \, + \, | \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \, + \, | ||
| - | \int_a^b \mathrm{ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{g} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 19: | Línea 19: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | La integral | + | La integral del producto de un número real <math> k </math> por una función es igual al producto de <math> k </math> por la integral de dicha función: |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Línea 32: | Línea 32: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | En una integral definida el limite superior de integraci\'on puede ser menor | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
que el limite inferior de integraci\'on y | que el limite inferior de integraci\'on y | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Línea 43: | Línea 40: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Si hacemos | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | a = b | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | en la igualdad anterior se tiene que | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \int_a^a \cdot \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \, = \, | ||
| + | - \cdot \int_a^a \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | como el único número que coincide con su opuesto es el cero, llegamos a la | ||
| + | conclusión de que | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \int_a^a \cdot \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \, = \, 0 | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | para cualquier número real | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | a | ||
| + | </math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dados tres números reales cualesquiera, | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | a, \, b, \, c | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | se tiene que: | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \int_a^c \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x = | ||
| + | \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x + | ||
| + | \int_b^c \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Si en el intervalo | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left[ \, a, \, b \, \right] | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | la función | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \mathrm{f} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | es mayor o igual que la función | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \mathrm{g} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | entonces | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \int_a^c \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \ge | ||
| + | \int_a^c \mathrm{g} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Si en el intervalo | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left[ \, a, \, b \, \right] | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | la función | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \mathrm{f} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | es mayor que la función | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \mathrm{g} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | entonces | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \int_a^c \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x > | ||
| + | \int_a^c \mathrm{g} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
[[Category: Matemáticas]] | [[Category: Matemáticas]] | ||
Revisión de 10:30 12 dic 2010
La integral de la suma de dos funciones es igual a la suma de las integrales de las funciones:
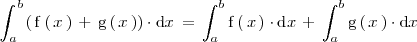
La integral del producto de un número realpor una función es igual al producto de
por la integral de dicha función:
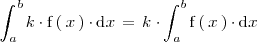
En una integral definida el limite superior de integraci\'on puede ser menor que el limite inferior de integraci\'on y
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
Si hacemos
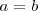 en la igualdad anterior se tiene que
en la igualdad anterior se tiene que
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
como el único número que coincide con su opuesto es el cero, llegamos a la conclusión de que
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
para cualquier número real
 .
.
Dados tres números reales cualesquiera,
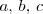 se tiene que:
se tiene que:
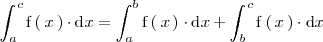
Si en el intervalo
![\left[ \, a, \, b \, \right]
\left[ \, a, \, b \, \right]](/images/math/math-bd2e5d8941aab87895e8817c63d00863.png) la función
la función
 es mayor o igual que la función
es mayor o igual que la función
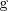 entonces
entonces
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
Si en el intervalo
![\left[ \, a, \, b \, \right]
\left[ \, a, \, b \, \right]](/images/math/math-bd2e5d8941aab87895e8817c63d00863.png) la función
la función
 es mayor que la función
es mayor que la función
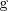 entonces
entonces
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]



