Definición de derivada
De Wikillerato
(Diferencias entre revisiones)
| (8 ediciones intermedias no se muestran.) | |||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| - | + | La derivada de la función | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \mathrm{f} | + | \mathrm{f} |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | | + | en el punto |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \ | + | x \, = \, a |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | , si | + | , si existe, es el valor del limite: |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Línea 27: | Línea 13: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, | + | \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, a \, + \, h \, \right) \, - \, |
| - | + | \mathrm{f} \left( \, a \, \right)}{h} | |
| - | </math> | + | </math>. |
</center> | </center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | | + | Si este limite es un número real, la función |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | \mathrm{f} | |
| - | \mathrm{f} | + | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | es '''''derivable''''' en | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | es | + | |
<math> | <math> | ||
x \, = \, a | x \, = \, a | ||
| - | </math> | + | </math>. |
| - | + | Si el límite anterior no es un número real o el límite no existe, la función | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
\mathrm{f} | \mathrm{f} | ||
| - | |||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | es | + | NO es derivable en |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | x = a | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</math>. | </math>. | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | La derivada de la función | |
<math> | <math> | ||
\mathrm{f} | \mathrm{f} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | en | |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | x | + | x = a |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | | + | se denota por |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | \mathrm{f}^\prime | |
| - | + | \left( | |
| - | + | \, a \, | |
| - | + | \right) | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | \mathrm{f}^\prime \left( \, a | + | |
</math>. | </math>. | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | <center> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| + | \mathrm{f}^\prime | ||
\left( | \left( | ||
| - | + | \, a \, | |
\right) | \right) | ||
| - | + | = \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, a \, + \, h \, \right) \, - \, | |
| - | + | \mathrm{f} \left( \, a \, \right)}{h} | |
| - | + | </math>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | </math> | + | |
</center> | </center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | == | + | ==Ejemplo 1== |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | Calculemos la derivada de | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| + | \mathrm{f} | ||
\left( | \left( | ||
| - | + | \, x \, | |
\right) | \right) | ||
| + | \, = \, x^2 | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | en | |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | x \, = \, 2 | |
| - | </math> | + | </math>: |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Línea 170: | Línea 91: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, | + | \mathrm{f}^\prime |
| - | + | \left( | |
| + | \, 2 \, | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | \, = \, \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, 2 \, + \, h \, \right) \, - \, | ||
| + | \mathrm{f} \left( \, 2 \, \right)}{h} \, = \, \lim_{h \to 0} \frac | ||
| + | {\left( \, 2 \, + \, h \, \right)^2 \, - \, 2^2}{h} \, = \, | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | \, = \, \lim_{h \to 0} | |
| - | \ | + | \frac {\left( \, 4 \, + \, 4h \, + \, h^2 \, \right) \, - \, 4}{h} \, = \, |
| + | \lim_{h \to 0} \frac {4h \, + \, h^2}{h} \, = \, \lim_{h \to 0} | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \, h \, + 4 \, \, | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | \, = \, 4 | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 199: | Línea 115: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | ==Ejemplo 2== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | La función | |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \mathrm{f} | + | \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) = \left| \, x \, \right| |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | es | + | NO es derivable en |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | x | + | x = 0 |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | | + | ya que no existe el limite |
| + | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | f | + | \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, 0 \, + \, h \, \right) \, - \, |
| + | \mathrm{f} \left( \, 0 \, \right)}{h} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | </center> | |
| + | No existe por que | ||
| + | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\mathrm{f}\left( \, 0 \, + \, h \, \right) \, - \, | |
| + | \mathrm{f} \left( \, 0 \, \right)}{h} = \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\left| \, h \, \right|}{h} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | </center> | |
| + | y por que | ||
| + | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \ | + | \lim_{h \to 0^-} \frac{\left| \, h \, \right|}{h} = -1 \neq 1 = |
| - | + | \lim_{h \to 0^+} \frac{\left| \, h \, \right|}{h} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | \ | + | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | </center> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | </ | + | |
| - | + | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | es decir, los dos limites laterales son distintos. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
[[Category:Matemáticas]] | [[Category:Matemáticas]] | ||
Revisión actual
La derivada de la función
 en el punto
en el punto
 , si existe, es el valor del limite:
, si existe, es el valor del limite:
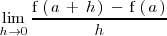 .
.
Si este limite es un número real, la función
 es derivable en
es derivable en
 .
Si el límite anterior no es un número real o el límite no existe, la función
.
Si el límite anterior no es un número real o el límite no existe, la función
 NO es derivable en
NO es derivable en
 .
.
La derivada de la función
 en
en
 se denota por
se denota por
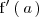 .
.
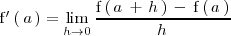 .
.
Ejemplo 1
Calculemos la derivada de
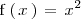 en
en
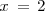 :
:
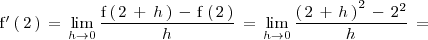
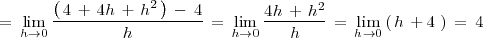
Ejemplo 2
La función
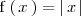 NO es derivable en
NO es derivable en
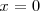 ya que no existe el limite
ya que no existe el limite
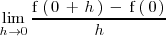
No existe por que
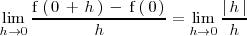
y por que
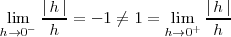
es decir, los dos limites laterales son distintos.



