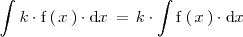Propiedades de las integrales indefinidas
De Wikillerato
(Diferencias entre revisiones)
| Línea 31: | Línea 31: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | La integral indefinida del producto de un número real <math> k </math> por una función <math> | + | La integral indefinida del producto de un número real <math> k </math> por una función <math> \mathrmf{f} </math> es igual al producto de <math> k </math> por la integral indefinida de la función <math> \mathrmf{}f </math>: |
| - | \mathrmf{f} | + | |
| - | </math> es igual al producto de <math> k </math> por la integral indefinida de la función <math> | + | |
| - | \mathrmf{}f | + | |
| - | </math>: | + | |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
Revisión de 18:15 27 dic 2010
Propiedad 1
La integral de la suma de dos funciones es igual a la suma de las integrales de las funciones:
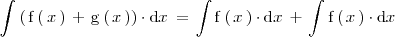
Propiedad 2
La integral indefinida del producto de un número realpor una función
es igual al producto de
por la integral indefinida de la función
: